KEY TAKEAWAYS
- Shell companies generally lack business activity, revenue, and assets, often having few, if any, staff members, with management potentially located in a different country.
- Despite their lack of traditional business operations, shell companies can offer advantages such as anonymity for owners, reduced taxes through offshore formations, and access to foreign markets.
- Shell companies are versatile in financial activities, being able to open bank accounts, engage in transactions, own intellectual property and real estate, differing fundamentally from traditional businesses that aim to generate revenue through goods or services.
What is a Shell Company?
Definition and Characteristics
A shell company is a business entity without significant assets or operational activities. Functioning as a vehicle for various financial maneuvers, these entities primarily exist as a name on legal documents. They often lack substantial physical presence or employees, which differentiates them from typical operating businesses. Shell companies focus on holding assets or managing other corporate structures rather than producing goods and services.
Common Legitimate Uses
Shell companies are not inherently illegal or suspicious. They are widely used for legitimate purposes such as asset protection against legal claims, facilitating international business by acting as holding companies, and engaging in mergers or acquisitions seamlessly, sometimes even playing a crucial role in a situational feat like a takeover. Another practical application includes setting up a special purpose acquisition company (SPAC), which is a type of issuer formed to raise capital through an initial public offering with the purpose of acquiring an existing company. These legal entities can also serve as investment holding structures that benefit from favourable tax treatments, illustrating their role as a tool in advanced trading and the broader category of business entities. Furthermore, businesses may use an offshore company to manage intellectual property rights efficiently, collecting royalties and managing business transactions, while considering tax implications with offshore bank and brokerage accounts. These uses underscore the importance of transparency and proper regulatory compliance, especially under laws like the Corporate Transparency Act, which mandates the reporting of ownership information.
Steps to Form a Shell Corporation Legally
Choosing the Right Jurisdiction
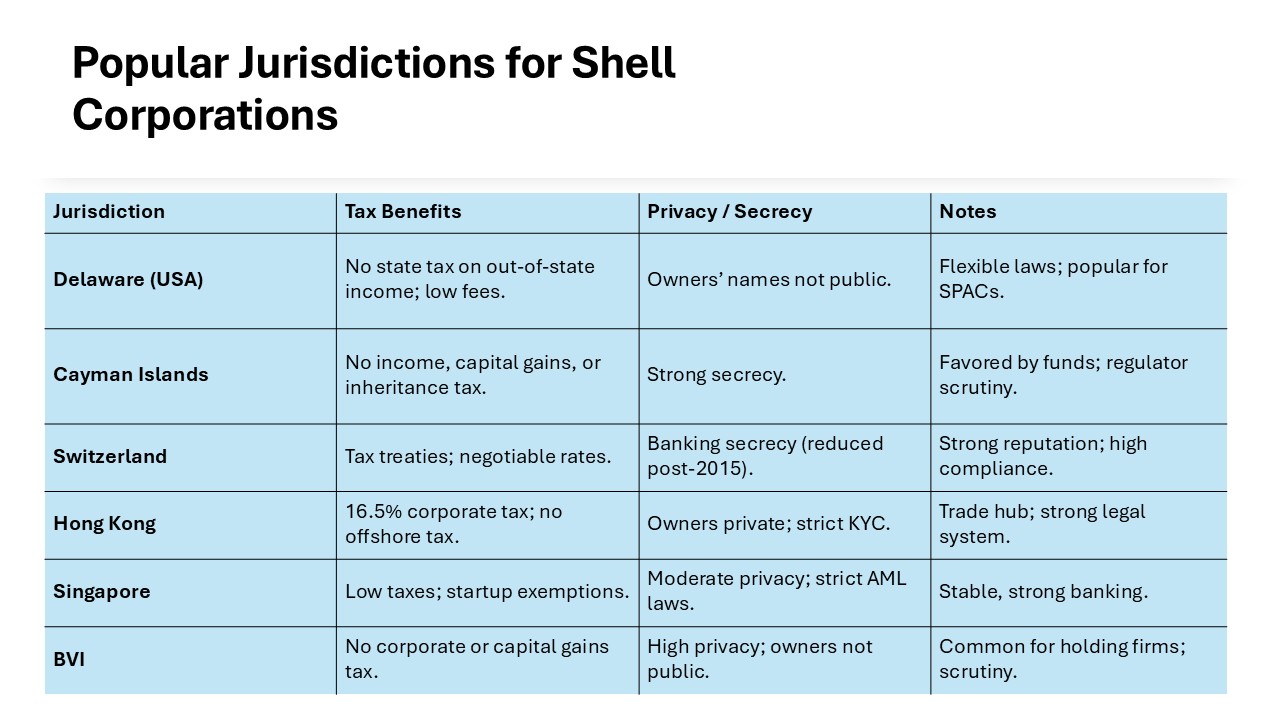
Selecting the right jurisdiction is pivotal when forming a shell corporation. Some countries or states, like Delaware in the United States, are popular due to favorable regulatory environments, including flexible corporate laws and attractive tax benefits. Every jurisdiction has different tax implications and privacy laws, so it’s essential to assess these factors in accordance with your business goals. Offshore companies can leverage these benefits significantly in terms of tax reduction and privacy enhancement. Another significant consideration is the level of financial secrecy and anonymity a jurisdiction offers, as this can impact your banking relationships and any offshore bank accounts you maintain. Nations such as Switzerland and Hong Kong are renowned for their traditions of banking secrecy, making them attractive options for tax avoidance strategies. Consulting with a legal expert to navigate these complexities can be exceedingly beneficial, especially given the close attention tax authorities pay to potential avoidance schemes. Additionally, creating a special purpose acquisition company (SPAC) can also be an effective strategy within the right jurisdiction.
Necessary Documentation and Compliance
Forming a shell corporation requires meticulous attention to documentation and compliance. You’ll start by preparing documents such as articles of incorporation, bylaws, and possibly operating agreements. Each jurisdiction may have specific paperwork requirements, so it’s important to verify these in advance. Ensuring compliance involves adhering to financial regulations, tax obligations, and ongoing statutory filings, all of which are essential under frameworks like the Corporate Transparency Act which aims to enhance corporate transparency and oversight. Utilizing professional services can streamline this process and help mitigate legal risks, especially when it comes to maintaining confidentiality and due diligence in compliance with accounting and tax obligations.
Registration Process Explained
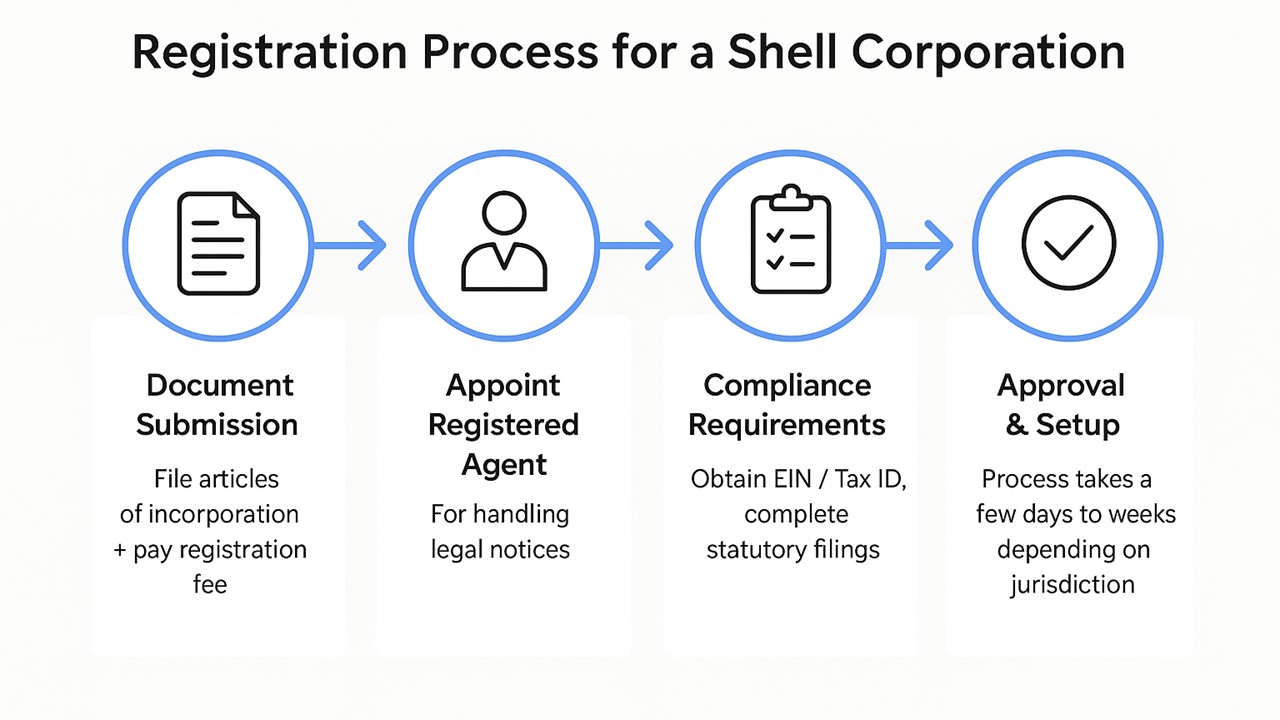
The registration process for a shell corporation typically begins with submitting the necessary documents to the relevant state or country authority. This often includes the articles of incorporation and a registration fee. Upon submission, you may need to appoint a registered agent who will handle legal correspondence. After filing, ensure timely completion of any additional compliance requirements, such as acquiring an employer identification number (EIN) or equivalent tax identification. The entire process can take anywhere from a few days to several weeks, depending on the jurisdiction.
Legal Considerations and Advice
Forming a shell company involves navigating numerous legal considerations. It is critical to ensure that the entity is used only for lawful purposes, adhering to both local and international regulations. Engaging legal counsel familiar with corporate law can provide invaluable advice, helping you avoid inadvertent violations that could lead to penalties or reputational damage. Proper legal structuring and continuous compliance checks are essential to use a shell corporation effectively and legally.
Regulatory Compliance and Oversight
Key Regulatory Bodies and Laws
Navigating the formation and operation of a shell company involves understanding the role of key regulatory bodies and pertinent laws. The U.S. government, for instance, often relies on the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN), and other state regulators to oversee corporate activity. Internationally, organizations like the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) set guidelines to combat money laundering. Each body enforces laws that promote financial transparency and integrity, such as the Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations. Compliance with these regulations is essential to prevent illegal activities and maintain legitimacy.
Maintaining Transparency and Record-Keeping
Transparency and meticulous record-keeping are fundamental to the lawful operation of a shell corporation. Under the Corporate Transparency Act, shell companies must report ownership information to the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN), a step to mitigate corruption. Maintaining detailed records of financial transactions, shareholder agreements, and board resolutions helps meet regulatory requirements and build trust with authorities. Regular audits and reviews facilitate compliance with financial regulations, ensuring all business dealings are above board. Digital solutions and software can simplify this process by organizing documentation and providing easy access for regulatory audits. Tracking transparency initiatives not only protects the corporation legally but also reinforces its reputation.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls
Avoiding common pitfalls when managing a shell company requires vigilance and proactive measures. One frequent mistake is neglecting compliance with tax and administrative filings, which can result in significant penalties. It’s crucial to establish robust internal controls to prevent misuse of the corporation for illegal activities such as tax evasion or money laundering. Additionally, engaging competent legal and financial advisors can provide guidance on maintaining transparency and regulatory adherence. Continuous education on evolving laws ensures that the corporation adapts appropriately, reducing the risk of non-compliance.
Advantages of Forming a Shell Corporation
Asset Protection Strategies
Shell companies can be strategically used for asset protection. By transferring ownership of valuable assets into a shell entity, you can safeguard them from potential lawsuits or creditors. This structure can also segregate assets from operating liabilities, reducing exposure to business risks. Implementing proper legal structures such as trusts or layered corporations enhances this protection. Always ensure compliance with relevant laws to avoid piercing the corporate veil, a situation where personal assets could be at risk if the corporation is found to be a mere facade.
Facilitating Cross-Border Transactions
Shell companies are frequently utilized to streamline cross-border transactions. By establishing a presence in multiple jurisdictions, such as Canada, Switzerland, and Hong Kong, these entities help navigate varying tax laws and regulations, potentially reducing tax liabilities through legal means. Additionally, employing an offshore company can protect assets and enhance privacy, although it is crucial to remain compliant with any taxes owed in your home country. They also provide a neutral platform for international partnerships, improving operational efficiency and financial flow.
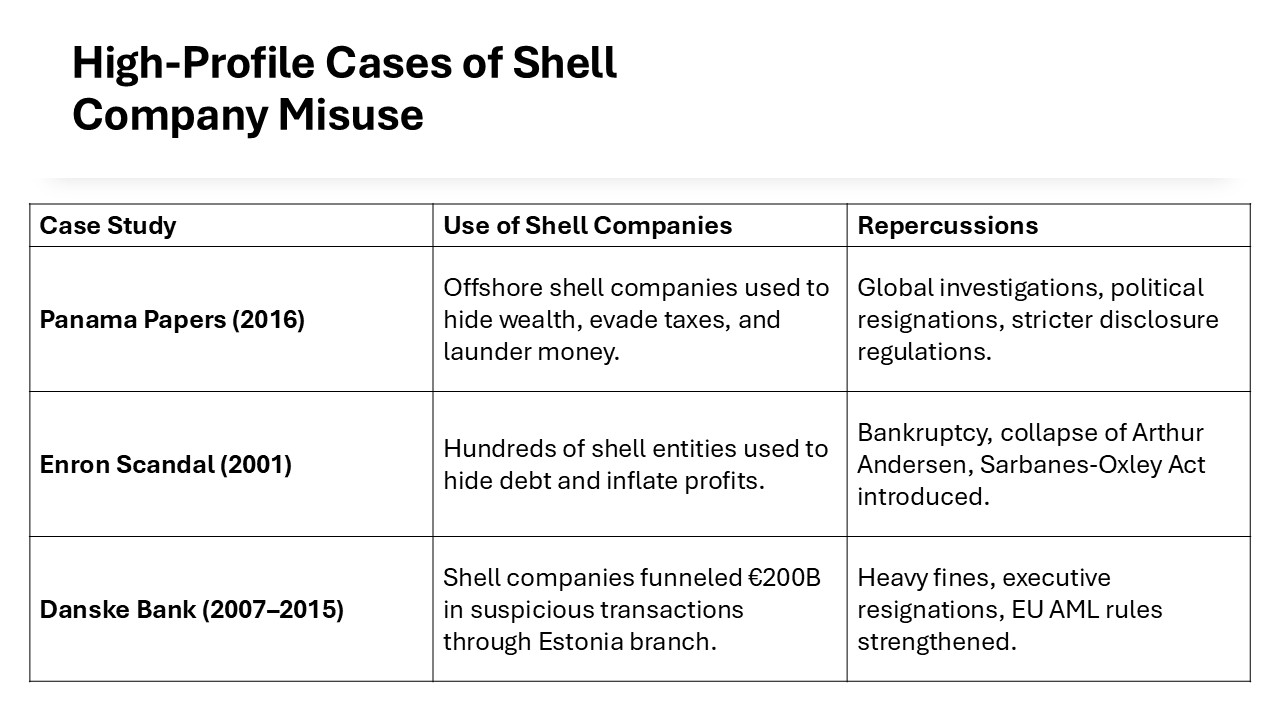
Notably, the Panama Papers leak has taught us that transparency is key, ensuring all business transactions are reported accurately to avoid legal scrutiny and accusations of corruption. While the term ‘shell company’ can often carry a negative connotation due to associations with financial secrecy, when used appropriately, they can serve legitimate purposes. For those considering offshore bank accounts, working with a financial advisor can ensure proper management and compliance. International trade deals can be complicated, so professional guidance is essential to ensure compliance with all applicable laws.
Risks and Misconceptions
Common Misunderstandings
Misunderstandings about shell companies often arise due to their association with illegal activities. Many assume all shell companies are inherently suspicious or used only for tax evasion, but numerous legitimate uses exist, from asset management to business restructuring. Another misconception is that shell companies are completely anonymous; however, jurisdictions increasingly require some level of transparency. Understanding the legal purposes and regulations governing these entities helps dispel myths and ensures compliance.
Risks Involved in Owning a Shell Company
Owning a shell company presents certain risks, primarily related to legal compliance and reputation. These entities can face increased scrutiny from regulatory bodies, especially if transparency levels are lacking or if they operate in high-risk jurisdictions. Non-compliance with anti-money laundering laws can lead to significant fines and legal challenges. Additionally, any perceived misuse can damage a company’s reputation, affecting stakeholder trust and business opportunities. Robust compliance measures and proper guidance can mitigate these risks.
Case Studies and Examples
Successful Legitimate Uses
There’s a range of successful legitimate uses for shell companies across various industries. For example, multinational corporations often use them to facilitate mergers and acquisitions. By holding shares or assets in a shell company, these businesses can streamline negotiations and transaction processes. Moreover, startups sometimes use shells to attract investors by simplifying ownership structures. These legitimate uses highlight how shell companies can be essential tools in strategic business planning.
Notable Legal Precedents
Legal precedents have significantly shaped the landscape surrounding shell companies. Landmark cases, such as certain SEC actions, have clarified compliance expectations and the importance of disclosure. In some instances, courts have pierced the corporate veil, holding individual owners accountable when shell companies were used for fraudulent purposes. These cases highlight the necessity of operating within legal boundaries and maintaining transparency to avoid personal liability.
FAQs
Is it legal to own a shell company?
Yes, it is legal to own a shell company as long as it is used for lawful purposes and complies with all applicable regulations, including transparency and tax laws. Utilizing expert legal guidance can ensure ongoing compliance.
Can you define shell company in simple terms?
A shell company is a business entity that doesn’t have active operations or significant assets. It’s often used to manage financial dealings or hold assets rather than conduct business activities.
How much does it cost to start a shell corporation?
The cost to start a shell corporation varies based on jurisdiction, typically ranging from a few hundred to a few thousand dollars. This includes registration fees, legal services, and initial setup costs.
Can a shell company own property?
Yes, a shell company can own property. This ownership can offer asset protection and tax advantages, but it’s crucial to ensure compliance with legal and tax obligations specific to property ownership.
What is the meaning of shell company in finance and business?
In finance and business, a shell company refers to a corporation with no significant operations or assets, often used for legal financial maneuvers like mergers, asset management, or protecting investments. It serves more as a corporate structure rather than an active business entity.
How do governments identify and regulate shell companies?
Governments identify and regulate shell companies through financial reporting requirements, beneficial ownership disclosures, and anti-money laundering regulations. Regulatory bodies cross-reference reported data with financial activity to ensure compliance and prevent illicit activities.