KEY TAKEAWAYS
- Net sales are not the same as revenue. While revenue reflects the total income of a company, net sales specifically account for sales revenue after subtracting returns, allowances, and discounts.
- Revenue provides a broad overview of all income streams, useful in financial statements for understanding overall sales activity. In contrast, net sales deliver more practical data on true profitability and operational efficiency by focusing solely on product sales.
- Both metrics serve distinct purposes; revenue is crucial for a company’s financial statements, offering a comprehensive image of income, while net sales are vital for analyzing sales strategies and deciphering true business income.
Unpacking Net Sales and Revenue
Definitions and Significance
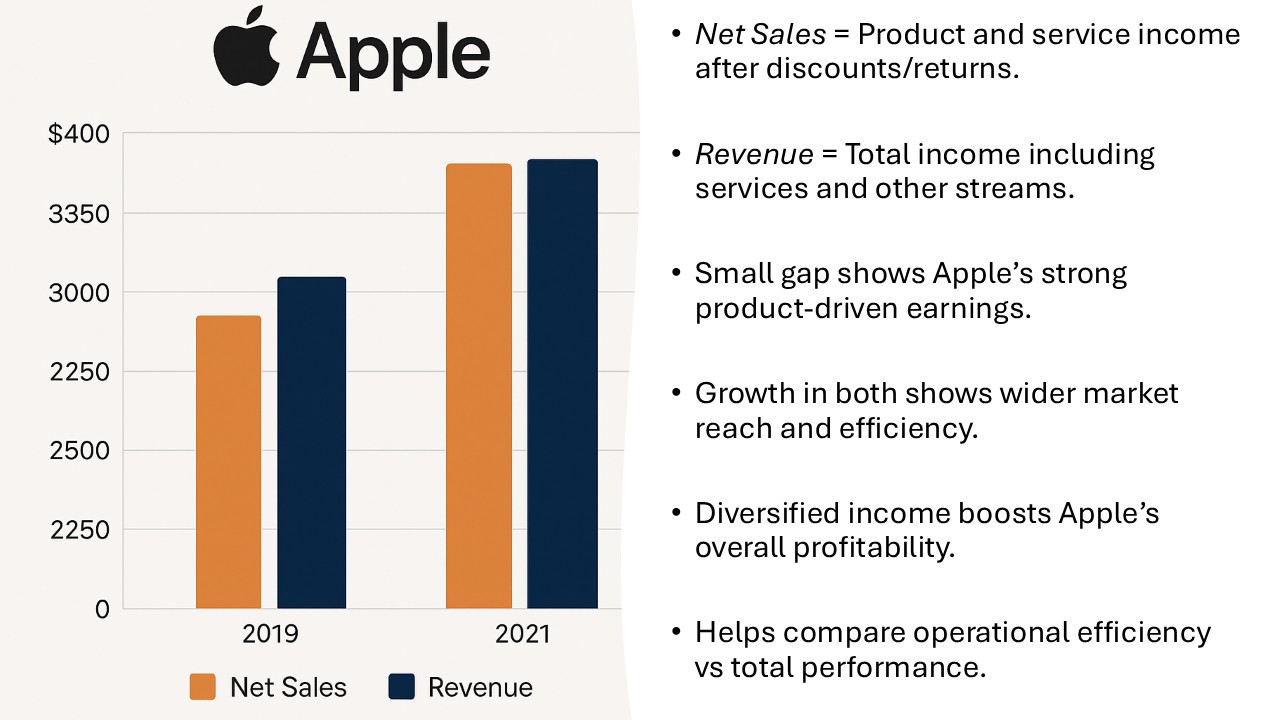
Net sales refer to the amount realized from selling goods or services after deducting returns, allowances, and discounts. It is a key indicator of a company’s effective sales strategies and customer satisfaction.
Revenue, on the other hand, encompasses all income generated from core business operations, which may include additional streams like investments or other business ventures. This broader metric signals the overall economic performance and growth potential of a company.
While net sales provide a clearer view of direct sales effectiveness, revenue offers a comprehensive outlook of a company’s total financial activity. These metrics together help in assessing both operational efficiency and broader market success.
Historical Context and Evolution
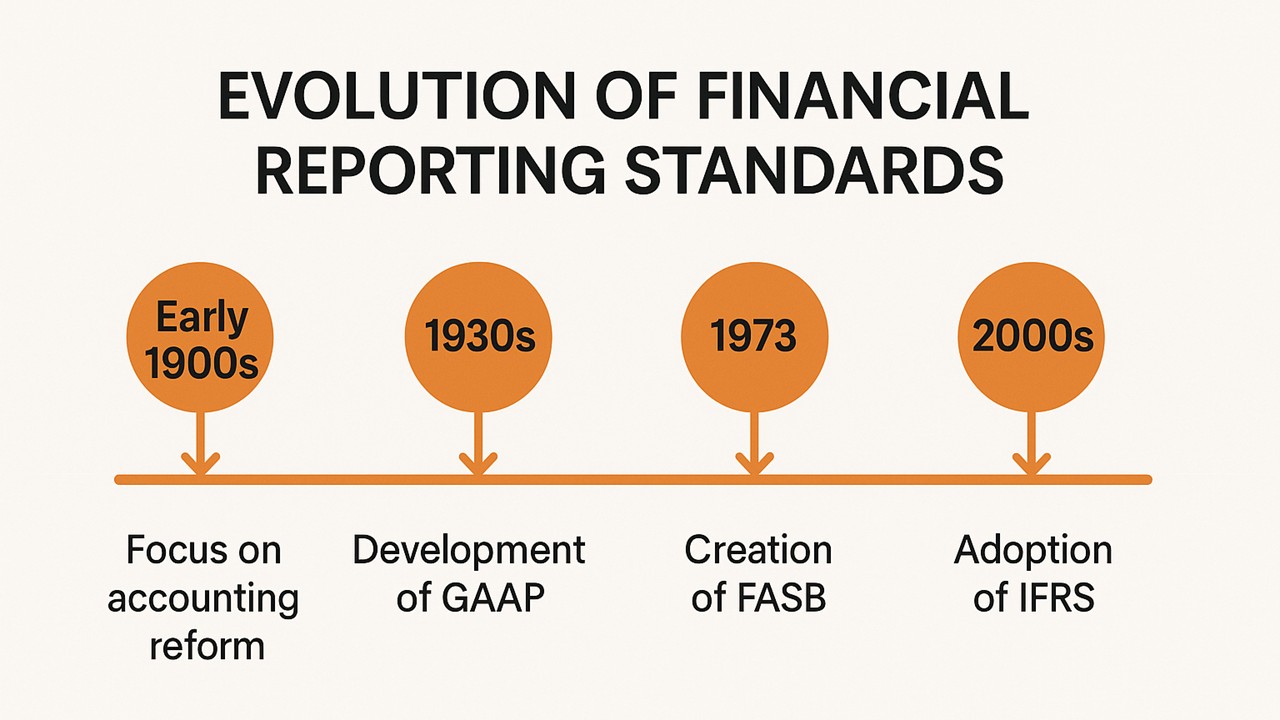
Historically, the differentiation between net sales and revenue has evolved as businesses expanded their scope and complexity. In the early days of commerce, companies only tracked gross sales due to simpler transaction processes. However, as markets globalized and business operations diversified, there arose a necessity to distinguish between gross sales, net sales, and total revenue.
The evolution was significantly influenced by the need for transparent financial reporting standards, dictated by organizations like the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB). Their guidelines ensure businesses accurately reflect financial realities, allowing clearer insights into performance and stability.
Understanding this evolution underscores the importance of these metrics in today’s business environment, where strategic planning relies heavily on detailed financial analysis.
Key Differences Between Net Sales and Revenue
Core Elements Distinguishing Each Metric
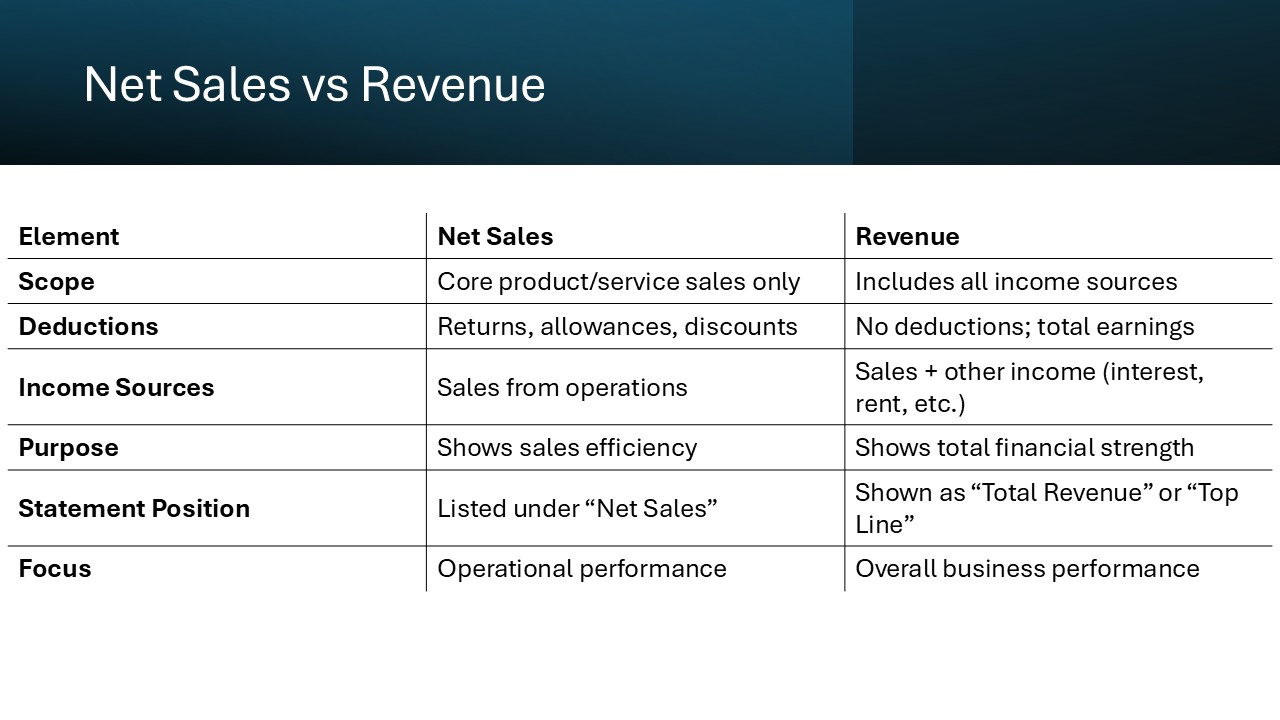
The primary elements distinguishing net sales from revenue revolve around scope and deductions. Net sales are specifically calculated from total sales minus returns, allowances, and discounts. This metric highlights the effectiveness of sales operations by showing the actual income from products or services sold. A high discrepancy between gross and net sales can be a red flag, indicating potential issues with revenue quality due to excessive discounting.
Revenue, however, is an all-encompassing figure that includes net sales but also integrates other income streams such as interest, dividends, and rental income. Thus, it provides a holistic view of the overall financial performance. Gross revenue is the total amount of money a business makes from selling its products or services before subtracting any costs, taxes, or other expenses. The Gross revenue amount is often referred to as the top-line revenue on the income statement.
The distinction is essential as net sales focus on core business transactions, while revenue reflects total economic activity. This enables companies to assess both their operational strengths and overall financial position. Setting targets using gross sales numbers is a popular way to go about this.
Real-world Applications and Examples
In practice, the distinction between net sales and revenue provides critical insights into different aspects of a business’s financial health. For example, a retail company may report high net sales, indicating successful inventory turnover and pricing strategies. However, if the overall revenue is significantly higher due to substantial investment returns, it suggests financial stability beyond just sales activities. Consider a tech company launching a new software product. Their net sales could reveal immediate customer response and market penetration, while revenue growth from ancillary services like technical support or software updates highlights long-term value creation and potential for a refund policy on subscriptions.
These applications help stakeholders make targeted decisions, such as optimizing sales tactics if net sales lag compared to total revenue growth. Viewing your MRR according to criteria like a client’s location and plan type can offer further strategic advantages.
The Impact on Business Financials
How Each Affects Profitability
Net sales directly impact profitability by highlighting the actual income generated directly from sales activities. When net sales increase, it usually signifies that more products were sold or pricing strategies were effective, both of which can lead to increased profit margins after covering production and operational costs.
Revenue, including all income sources, provides a broader profitability picture. Higher revenue due to diversified income streams can lead to increased net profits, even if a company faces decreased net sales. This broader approach can mitigate risks associated with fluctuations in core sales.
Therefore, while net sales give insight into sales performance, revenue analysis is crucial for understanding and planning overall profit strategies.
Influence on Financial Planning
In the realm of financial planning, both net sales and revenue play pivotal roles. Net sales data allow businesses to fine-tune their sales strategies, adjust pricing, and manage inventory effectively to optimize future income. They form the backbone of forecasting models aimed at improving sales efficiency and market presence.
Revenue influences broader strategic planning. It encompasses not only sales performance but also the effectiveness of additional income streams. By analyzing revenue trends, companies can identify diversification opportunities, allocate resources wisely, and assess the viability of expanding into new markets or investing in new initiatives.
In essence, while net sales drive operational strategies, revenue guides long-term financial planning, ensuring sustainable growth and stability
Measuring and Calculating Metrics
Understanding the Calculation Formulas
Understanding the distinct calculation formulas for net sales and revenue is crucial for accurate financial analysis.
For net sales, the formula is straightforward:
Net Sales = Gross Sales – Returns – Allowances – Discounts
This formula focuses on the core income from sales activities, providing a clear view of effective revenue from customers after accounting for any deductions.
On the other hand, revenue encompasses a broader range of income components:
Revenue = Net Sales + Other Income (e.g., royalties, interest, dividends)
This comprehensive formula includes all income streams, offering a larger picture of overall financial performance.
Accurate application of these formulas enables precise financial assessment and strategic planning.
Tools and Techniques for Accurate Tracking
To ensure precise tracking of net sales and revenue, leveraging modern financial tools and techniques is essential. Accounting software like QuickBooks and SAP provides integrated platforms for real-time data entry, automated calculations, and insightful reports. These tools can track sales transactions, manage customer returns, and tally income from various data sources efficiently. It’s vital to integrate verification processes to enhance the accuracy of your sales data by regularly checking for discrepancies and validating your system’s outputs.
Additionally, utilizing dashboard tools such as Tableau or Power BI can offer visual insights into sales and revenue trends. These platforms enable businesses to depict complex data clearly through charts and graphs, facilitating easier interpretation and decision-making. Tracking gross sales using these tools helps in evaluating sales performance over different periods. For enhanced accuracy, implementing data analytics techniques can help identify patterns, predict future sales trends, and enhance revenue forecasting.
Businesses often employ various accounting methods to categorize revenue streams, including passive income from referrals or partnerships, ensuring accurate financial reporting. Regular audits further ensure data integrity and compliance with financial reporting standards.
By combining these tools and techniques, companies can achieve thorough and accurate tracking of net and gross sales and revenue.
Case Studies and Industry Comparisons
Success Stories from Leading Companies
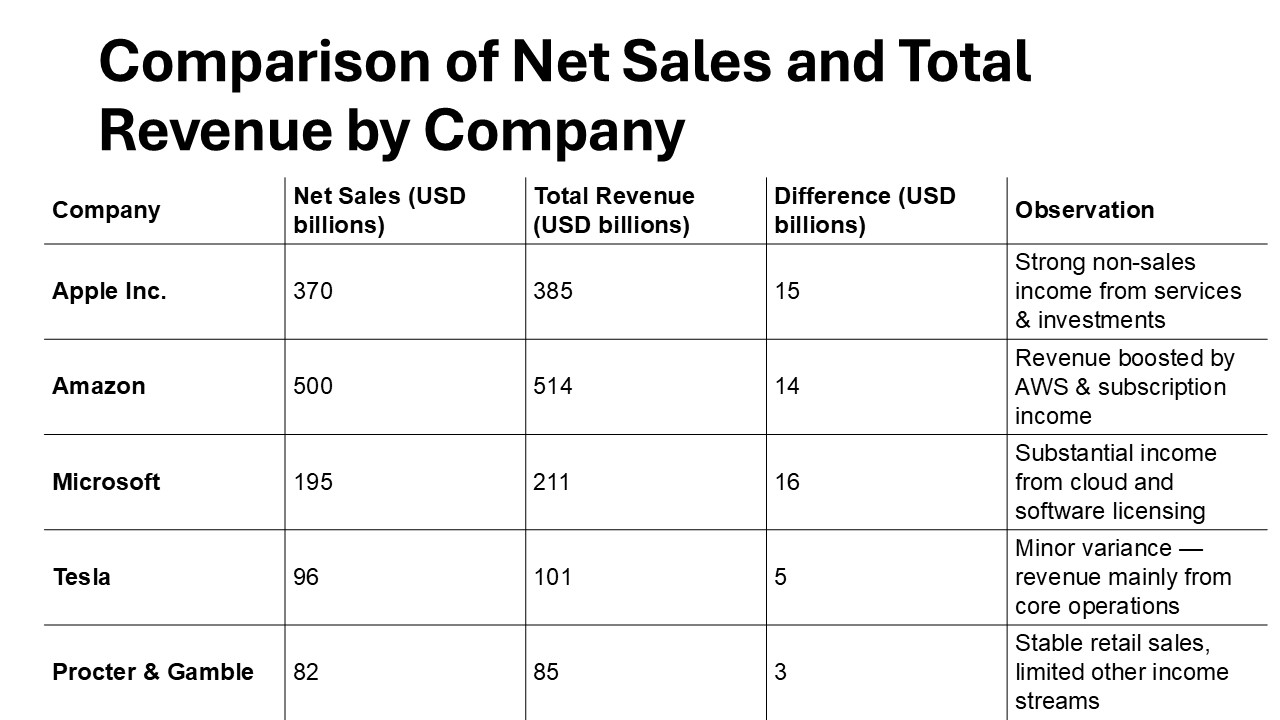
Several leading companies have effectively leveraged the distinctions between net sales and revenue to bolster their success. For instance, Apple meticulously tracks its net sales from product lines, enabling them to optimize production and marketing strategies. By honing in on strong net sales metrics, they have been able to enhance product launches and customer engagement.
Amazon, in contrast, showcases a powerful use of diverse revenue streams. Beyond its e-commerce net sales, Amazon captures substantial revenue through Amazon Web Services (AWS). This diversification not only boosts Amazon’s financial stability but also allows them to invest in innovation and expansion across various sectors.
These success stories highlight how understanding and applying the nuances between net sales and revenue can drive strategic growth and ensure long-term profitability.
Common Mistakes and Lessons Learned
Businesses often make critical errors when failing to differentiate between net sales and revenue. One common mistake is overestimating profitability by focusing solely on gross sales without accounting for returns or discounts, leading to misleading financial projections.
Another frequent error is neglecting other revenue streams. Companies that rely too heavily on their core sales, overlooking opportunities for diversification, may miss out on substantial additional income.
A key lesson learned from industry leaders is the importance of integrating comprehensive financial analysis. Tracking both net sales and total revenue allows for better strategic planning, risk management, and competitive advantage.
For instance, a retail chain might learn that inflated gross sales figures don’t translate to higher net sales due to excessive markdowns—prompting a reassessment of pricing strategies.
Leveraging Differences for Business Growth
Strategies to Optimize Both Metrics
Optimizing both net sales and revenue requires targeted strategies tailored to each metric.
Optimizing both net sales and revenue requires targeted strategies tailored to each metric. For enhancing net sales, focus on improving sales tactics and reducing customer returns. This can be achieved through training sales teams, refining marketing efforts, and ensuring product quality. Offering limited-time discounts and personalized promotions can also boost direct sales while managing discount magnitude to maintain profitability.
To increase overall revenue, consider diversification strategies. Explore new markets, enhance product lines, or develop additional services. Investing in new technologies can create additional income streams—such as licensing fees, ad-based revenue, or partnerships. Furthermore, leveraging customer feedback to enhance product offerings and customer service can help reduce churn and ensure consistent revenue growth.
By balancing strategies that address both core sales and broader income generation, businesses can enhance their financial health and sustain long-term growth. Such strategies also require consideration of customer consent to use data-driven insights effectively and ethically.
Improving Sales Performance Using Analytics
Applying analytics to improve sales performance involves utilizing data-driven insights to refine sales strategies and predict customer behaviors. By analyzing sales data, businesses can identify high-performing products, understand customer preferences, and detect patterns in buying behavior, leading to more effective targeting. Incorporating these strategies not only enhances loyalty among existing customers but can also boost overall productivity in sales operations.
Implement predictive analytics to forecast sales trends and adjust inventory accordingly. This helps prevent stockouts or excess inventory, optimizing sales opportunities and operational efficiency. Also, use customer segmentation analytics to customize marketing efforts, delivering personalized messages that resonate with different consumer groups. Including such tailored content on your website or blog can further strengthen customer loyalty and engagement.
Monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) like conversion rates and customer acquisition costs through analytics tools can pinpoint areas needing improvement, ensuring resources are directed efficiently. Ultimately, integrating a robust analytics strategy enhances decision-making and supports sustained sales growth.
FAQs
Is sales the same as total revenue?
No, sales refer to the revenue generated from selling goods or services, while total revenue includes sales as well as other income streams like investments and interest. Sales are a component of total revenue, but total revenue provides a broader view of a company’s financial activities.
What is the main difference between net sales and revenue?
The main difference between net sales and revenue is scope. Net sales focus on income from selling goods or services after deducting returns, allowances, and discounts. Revenue encompasses net sales and includes additional income from other sources, providing a comprehensive picture of total economic activity.
How do companies report net sales and revenue differently?
Companies report net sales and revenue differently by distinguishing them in their financial statements. Net sales are typically reported as the top line of the income statement, highlighting sales deducted for returns and discounts. Revenue appears as the total figure, encompassing net sales and all other income sources, offering a complete financial overview.
Why is it crucial to distinguish between these two metrics?
Distinguishing between net sales and revenue is crucial because it provides clearer insights into a company’s operational efficiency and overall financial performance. Net sales help assess the effectiveness of sales strategies, while revenue offers a broader view, including diversified income streams, aiding in informed strategic planning and decision-making.
Are sale vs revenue terms interchangeable in accounting?
No, sales and revenue terms are not interchangeable in accounting. Sales specifically refer to income from selling goods or services. In contrast, revenue includes sales and other income sources like interest or investments, thus offering a broader financial perspective.