KEY TAKEAWAYS
- Terminology and Meaning: Net earnings and net income are interchangeable terms referring to the bottom line on an income statement, showcasing a company’s total profit after all expenses, taxes, and costs are deducted.
- Role in Financial Analysis: Both metrics serve as indicators of operational performance and financial health, providing insights into cost management, operational efficiency, and revenue generation capabilities.
- Impact on Business and Investment Decisions: Positive and growing net earnings/income can enhance a company’s attractiveness to investors, boost its creditworthiness, improve access to financing, and support overall business expansion.
Defining Net Earnings vs Income
What Are Net Earnings?
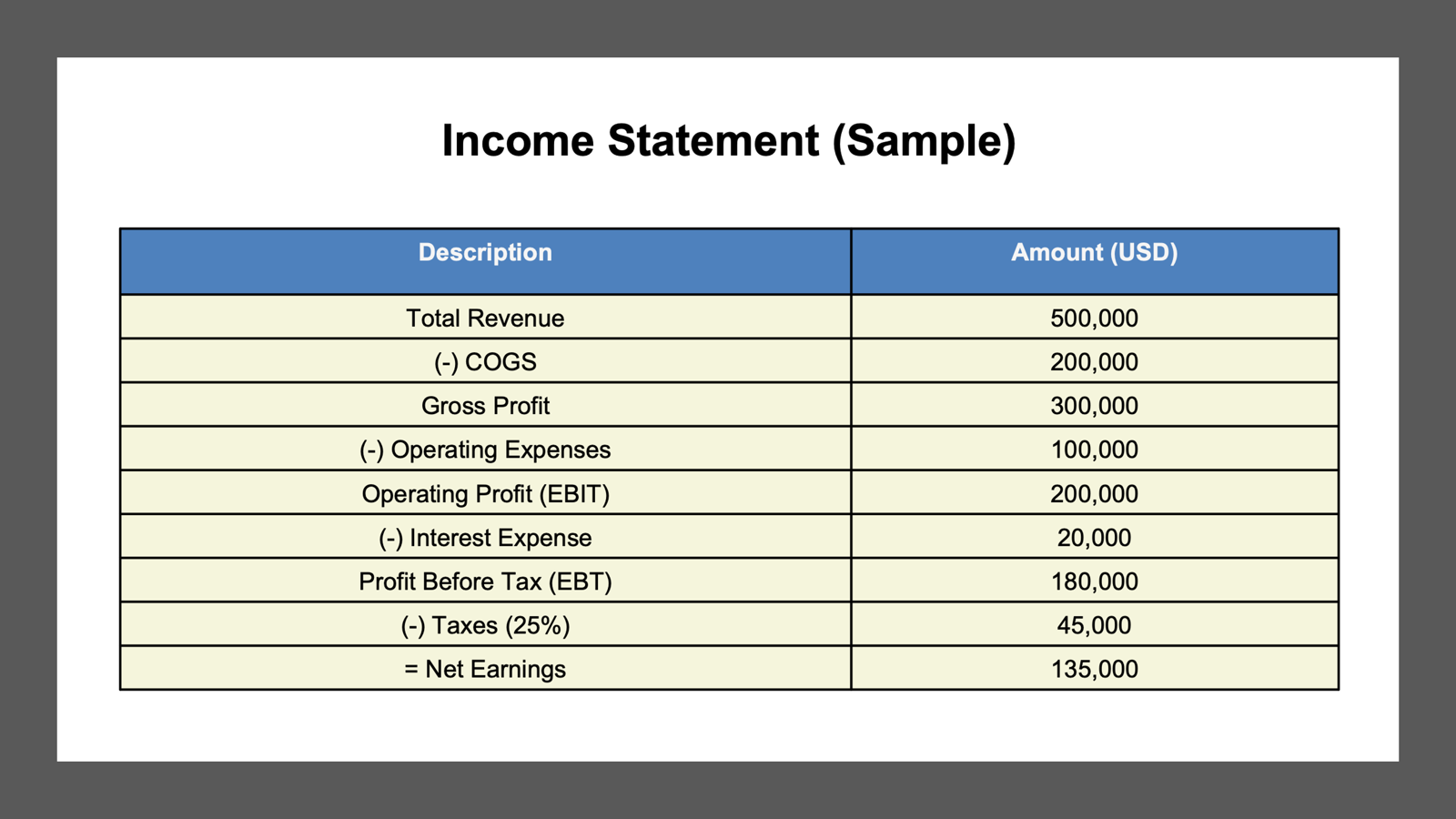
Net earnings, often referred to as net profit or net income, represent the total profit of a company after subtracting all expenses, taxes, and costs from total revenue. This encompasses deductions like payroll and state income taxes, signifying the actual financial gain. Moreover, net earnings are a critical indicator of a company’s profitability and financial efficiency, as they are typically reported at the bottom of an income statement. Including factors such as non-operating expenses and allowances, a positive net earnings figure signifies that a company has exceeded its operational and administrative costs. Additionally, net earnings can be described as the revenue minus expenses and taxes, which make up the taxable income.
Understanding Income
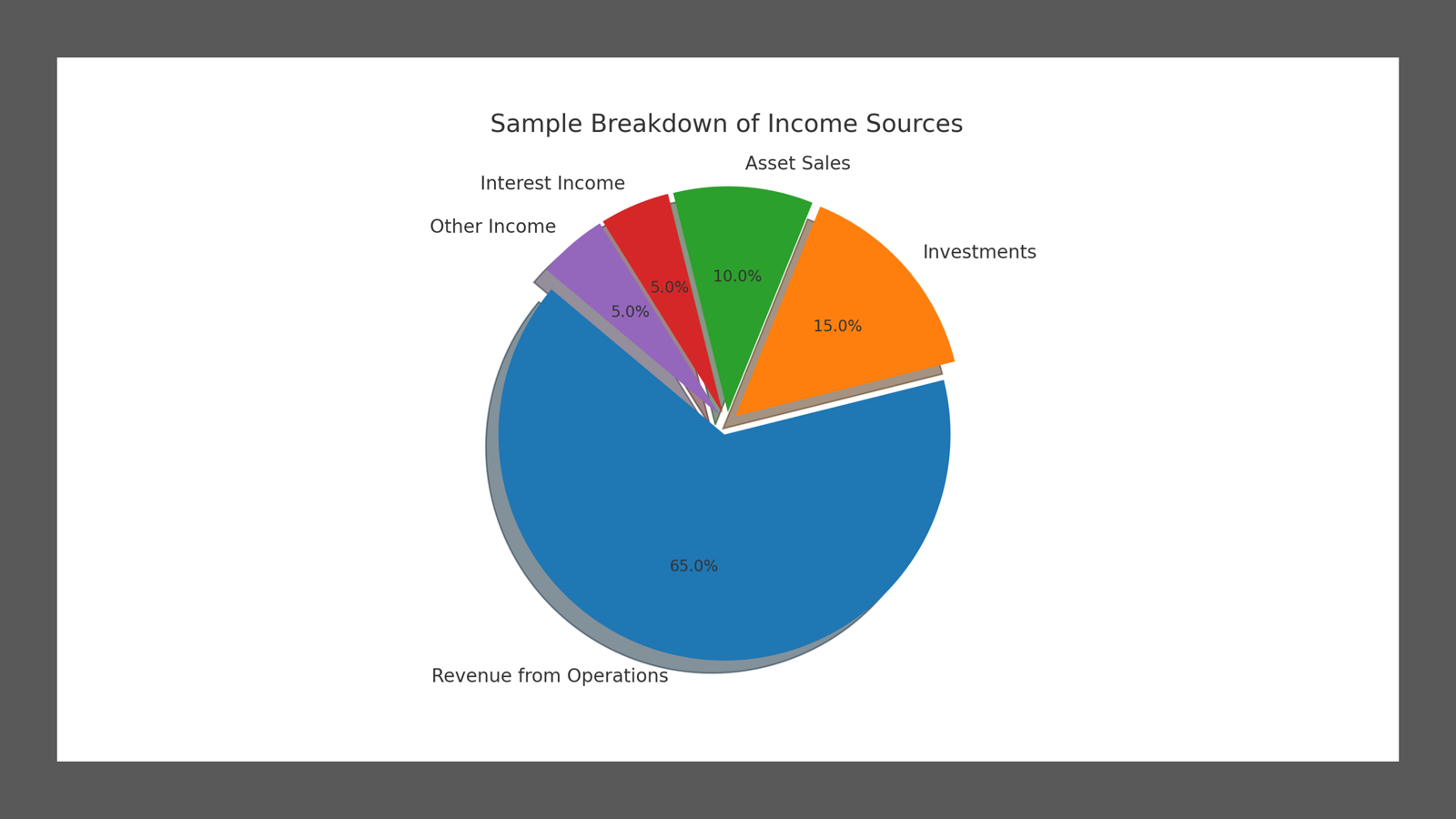
Income is a broader term encompassing all the money received by a business. This includes revenue from core operations and other sources such as investments, asset sales, or interest income. While net earnings dive into profits, income captures all inflows without accounting for the expenses or liabilities. Understanding income is crucial as it provides a complete picture of a company’s revenue-generating activities.
Key Differences Between Net Earnings and Income
Gross vs. Net: A Common Confusion
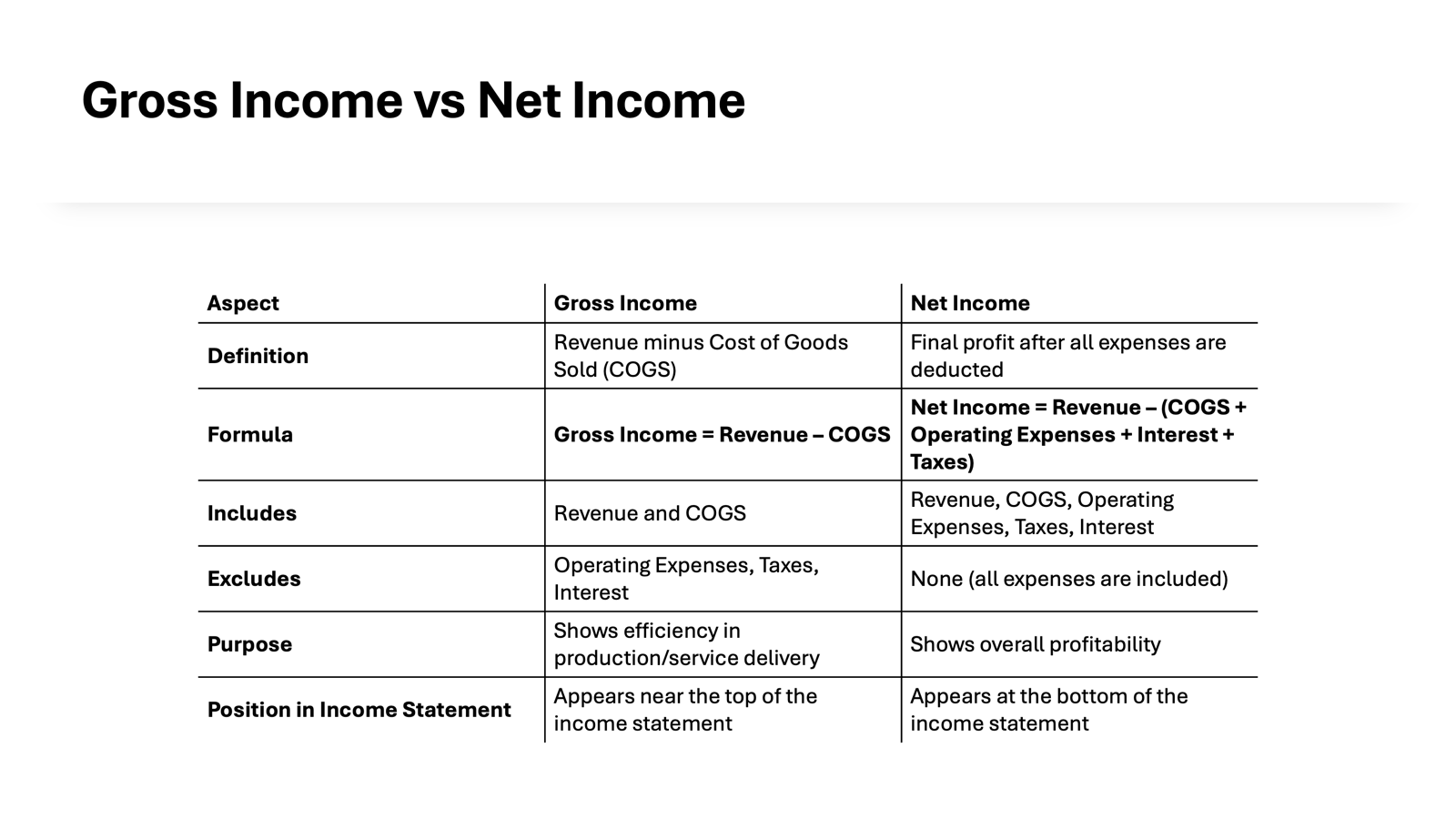
Gross income and net income often create confusion, as they represent different stages of a company’s financial cycle. Gross income, or gross profit, is the total revenue minus the cost of goods sold (COGS). It doesn’t take into account operating expenses, taxes, or other deductions.
Conversely, net income reflects the actual profit after all expenses have been deducted, including taxes, interest, and operational costs. Essentially, gross income reveals how well a company manages its production or service costs, while net income indicates the company’s overall profitability.
How Net Income Reflects Cash Flow
Net income is a fundamental component of cash flow analysis, though it differs from cash flow itself. It includes non-cash expenses like depreciation and adjustments for accounts receivable and payable. This means while net income includes potential earnings, cash flow focuses on actual cash available to a business. A company with strong net income but poor cash flow may struggle to cover immediate expenses, highlighting the importance of both metrics for financial health. Comprehensive financial analysis often considers both net income and cash flow to assess a company’s liquidity and operational efficiency. This analysis also accounts for non-operating activities such as leasing or investments, which might affect gross income minus expenses. Calculating net revenue requires subtracting returns, discounts, and allowances from total sales, which can further illuminate the company’s true earnings potential alongside amortization expenses.
The Significance in Financial Statements
Role in Business Performance Evaluation
Net earnings play a pivotal role in evaluating business performance. By assessing net earnings over time, stakeholders can determine profitability trends and operational efficacy. A rising net earnings trend typically indicates an improving business strategy, effective cost management, and increased revenue generation.
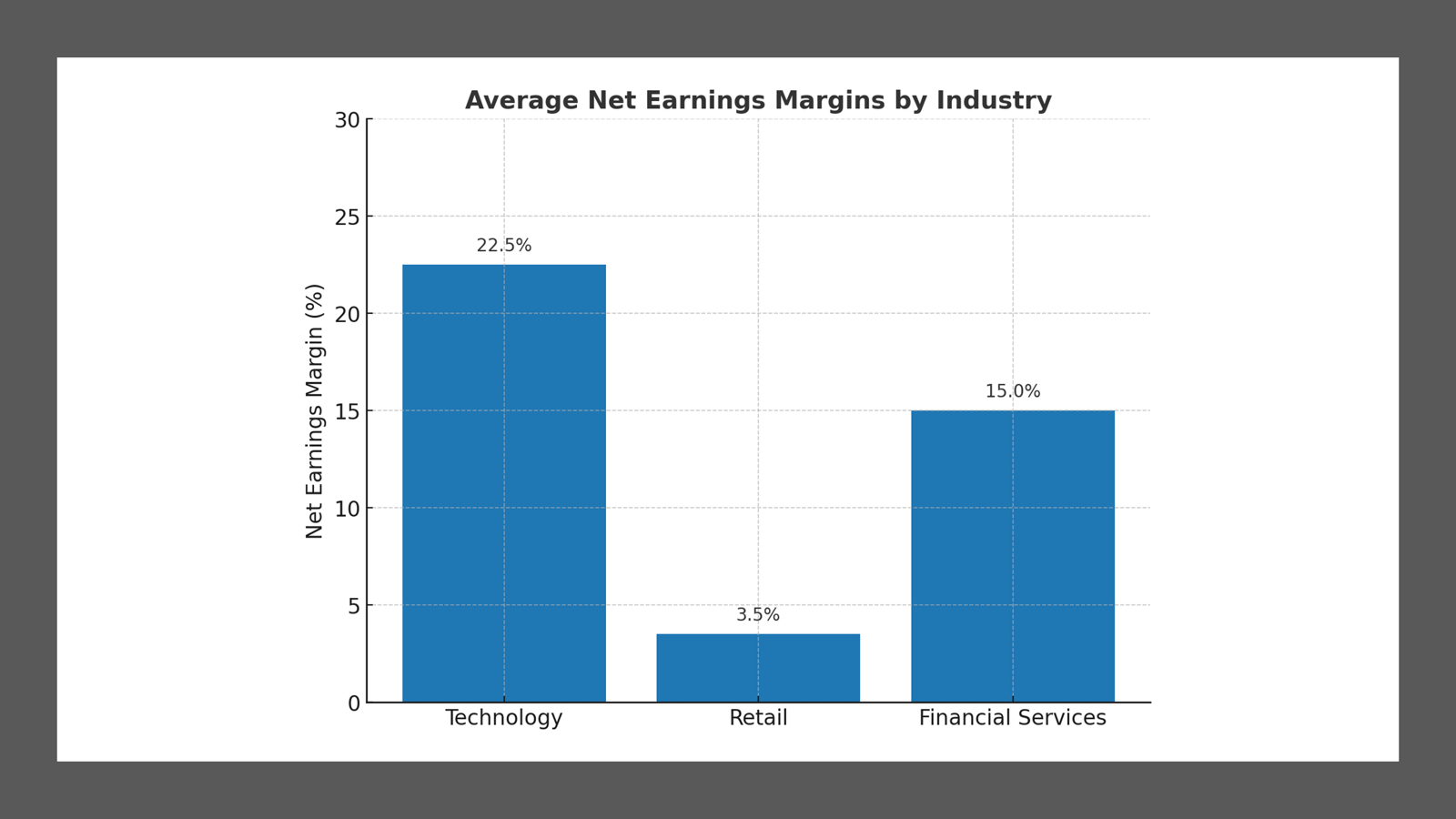
Additionally, comparing net earnings against industry benchmarks can provide insights into competitive standing and market positioning. Investors often view consistent net earnings growth as a positive indicator of a company’s long-term viability.
Impact on Bottom Line and Cash Reserves
Net earnings, synonymous with net income, directly influence a company’s bottom line, serving as a crucial business metric of profitability. High net earnings contribute to stronger cash reserves, offering financial stability and flexibility in decision-making. These reserves allow businesses to invest in growth opportunities, weather economic downturns, and maintain shareholder payouts. However, low net earnings could signal insufficient revenue generation or high operating costs, potentially jeopardizing the business’s financial health, even when amortization is factored into the valuation. Moreover, expenses such as overhead—which include payroll, marketing, and office expenses—can significantly affect the net income, as noted by financial insight platforms like Investopedia. By monitoring how net earnings affect cash reserves, companies can strategize for long-term sustainability and ensure the balance between operating and non-operating earnings.
Calculation and Reporting
How to Calculate Net Earnings
Calculating net earnings involves subtracting total expenses from total revenue. The formula is straightforward:
Net Earnings = Total Revenue – Total Expenses.
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown:
- Determine Total Revenue: Calculate all income from sales and services.
- Subtract Costs of Goods Sold (COGS): These include direct costs related to production.
- Subtract Operating Expenses: Include salaries, rent, utilities, and marketing costs.
- Factor in Taxes and Interest: Deduct payments made for interest and taxes.
This process provides the net earnings figure, reflecting the actual profit or loss during a specified period.
Effective Ways to Track Income
Tracking income effectively requires robust systems and methodologies to capture all inflows accurately. Here are some strategies you might consider:
- Use Accounting Software: Tools like QuickBooks or Xero automate income recording and reporting, offering real-time insights.
- Maintain Accurate Records: Keep detailed invoices and receipts to track both expected and received payments.
- Regular Reconciliation: Frequently compare income records with bank statements to ensure accuracy and identify discrepancies.
- Segment Income Sources: Categorize income by type, such as operating revenue, investment income, and other earnings, for clearer insights.
- Monitor Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Focus on metrics such as average income per customer and income growth rate to assess performance trends.
Implementing these practices ensures that businesses maintain a clear understanding of their income, aiding in financial planning and strategy.
Misconceptions and Myths
Revenue Always Equals Profit
A common misconception is that revenue always equals profit. In reality, revenue is merely the total income generated from business activities before expenses. Profit, specifically net profit, accounts for all expenses, taxes, and costs. Therefore, high revenue doesn’t necessarily translate to a high profit. Businesses can have substantial revenue yet still incur losses if their costs outweigh their income. Understanding this distinction is vital for accurate financial analysis and strategic planning.
High Net Income Indicates Business Success
High net income is often seen as a hallmark of business success, but it’s not the sole indicator. While it reflects profitability, it doesn’t automatically imply financial health or potential for growth. Other factors like cash flow, market competition, and debt levels also play crucial roles. A company might report high net income, yet struggle with cash management or suffer from rising debts. Therefore, evaluating a business’s success necessitates a comprehensive approach beyond just net income figures.
Practical Application in Business Analysis
Using Metrics to Guide Investment Decisions
Investors often rely on a suite of financial metrics to inform their investment decisions. Key among these is the Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratio, which compares a company’s share price to its earnings per share, indicating expected growth. Additionally, Return on Equity (ROE) measures how efficiently a company uses shareholders’ equity to generate profit. Debt-to-Equity ratio further informs about financial leverage, signaling how much debt is used to finance assets. By combining these metrics with the net earnings figures, investors can assess a company’s profitability, growth potential, and financial health, guiding smarter investment choices. Moreover, understanding gross profit, EBITDA, and cash flow as business metrics is crucial, particularly in fintech sectors where financial manipulation might skew traditional metrics.
Importance in Budget Planning
Net earnings are crucial in budget planning, serving as a foundation for financial forecasting and resource allocation. With a clear understanding of net profits, businesses can set realistic budgetary goals and prioritize expenditure areas. It helps in planning for capital investments, operational expenses, and setting aside reserves for emergencies.
Effective budget planning with an eye on net earnings ensures that business operations remain sustainable and aligned with strategic growth objectives. This approach can also help identify potential cost savings and investment opportunities.
FAQs
Are net earnings considered the same as net income?
Yes, net earnings and net income refer to the same financial measure. Both represent the profit a company has after all expenses, including taxes and operating costs, are deducted from total revenue. They provide insight into a company’s profitability.
How do net earnings impact a company’s financial health?
Net earnings significantly impact a company’s financial health by indicating its ability to generate profit after expenses. Strong net earnings enhance cash reserves, enable reinvestment, and improve creditworthiness, while weak earnings could signal potential financial struggles and limit growth opportunities.
Why are net earnings important for small businesses?
Net earnings are crucial for small businesses as they reflect profitability and operational efficiency. They guide financial planning, influence funding opportunities, and help assess growth potential. Healthy net earnings can attract investors and secure loans, vital for expansion and sustainability.
What is the difference between net profit versus net income?
There is no difference between net profit and net income; both terms are used interchangeably to describe the same financial metric. They signify the profit remaining after all expenses, taxes, and costs have been deducted from total revenue, showcasing the company’s profitability.