KEY TAKEAWAYS
- Bookkeepers play a crucial role in maintaining the daily financial transactions of a business, ensuring a steady flow of finances in and out of the entity.
- Unlike accountants, bookkeepers do not require an undergraduate degree; instead, their primary focus is on accuracy, consistency, and minimizing errors in financial records.
- Proficiency in accounting software and technological literacy is essential for bookkeepers, as they handle hundreds of financial transactions and provide foundational data for strategic financial planning.
Understanding the Role of a Bookkeeper
Defining the Bookkeeping Profession
Bookkeeping is the process of recording and managing all financial transactions of a business. This profession, often associated with the bookkeeper noun, is pivotal to maintaining an organized and accurate record of a company’s financial activities. Bookkeepers ensure that every financial transaction, from sales revenue to expenses and payroll, is documented meticulously. In the modern era, bookkeeping machines have significantly enhanced the efficiency and accuracy of this process, akin to how classic games like Scrabble have transitioned from board to digital formats while retaining their core elements. Their work forms the backbone of accurate financial reporting, making it easier for businesses to understand their financial position and comply with regulatory requirements. According to Cambridge University Press, integrated financial systems resemble a robust game plan, crucial for business success and fraud prevention.
Why Bookkeepers Are Essential for Businesses
Bookkeepers are crucial for businesses as they ensure financial accuracy and organization. They provide detailed, up-to-date payroll records which are vital for the overall accounting process and enable business owners to make informed decisions. Accurate bookkeeping helps in budget planning, forecasting, and financial analysis. Additionally, meticulously maintained records are essential for tax reporting and compliance, thus avoiding potential legal issues. Bookkeepers also facilitate smoother audits and financial inspections by maintaining transparent and structured records, thus streamlining the entire accounting process.
Key Responsibilities of a Bookkeeper
Daily Duties and Tasks
Bookkeepers are tasked with a range of daily duties that keep a business’s financial operations running smoothly. Typical tasks include recording financial transactions, which often involves data input into bookkeeping machines for accuracy and efficiency. Monitoring accounts payable and receivable, managing expense reports, and reconciling bank statements ensure that records align with actual financial activity. This role often involves compiling data for monthly and quarterly reports, which are crucial for business assessment and strategy planning.
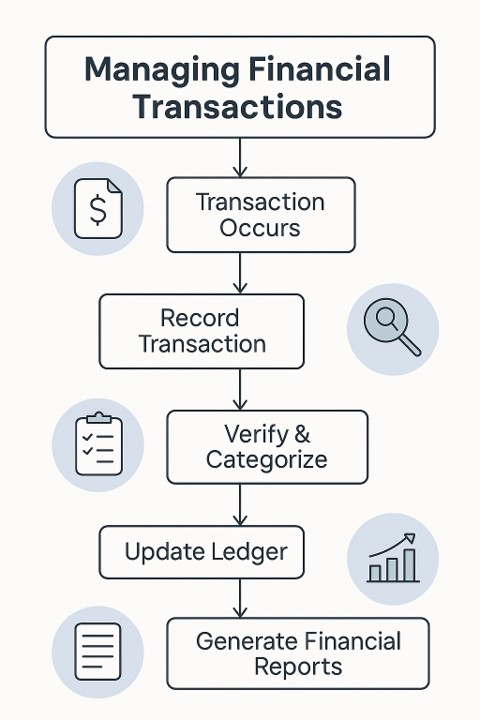
Managing Financial Transactions
Managing financial transactions is a core responsibility for bookkeepers, involving the meticulous documentation of every financial movement within a business. This role includes processing invoices, receiving payments, and ensuring that each transaction is recorded correctly. Bookkeepers must verify the accuracy of transaction details and categorize them within the financial system to maintain organized accounts. This management extends to tracking cash flow, addressing discrepancies swiftly, and ensuring that ledgers reflect real-time financial standing.
Maintaining Accurate Records
Maintaining accurate records is a critical duty for bookkeepers and involves consistently updating and organizing financial information. This task requires careful attention to ensure all financial documents, including receipts, invoices, and statements, are categorized and stored properly for easy retrieval. Bookkeepers must regularly audit records to prevent errors and fix any discrepancies promptly. Accurate records form the basis of financial reporting, aid in tax filing, and support sound business decisions by providing a clear picture of fiscal health.
Skills Required to Be a Successful Bookkeeper
Attention to Detail
Attention to detail is a paramount skill in bookkeeping, as precision is key when handling financial data. Bookkeepers must carefully check every entry and transaction to ensure that they reflect the actual financial activities of the business. Even minor errors can lead to significant discrepancies, affecting financial decisions and reporting. A vigilant approach helps prevent mistakes that could lead to financial loss or legal trouble, ensuring records are reliable and accurate at all times.
Analytical Skills
Analytical skills are essential for bookkeepers to interpret and make sense of financial data. They must assess financial documents to identify patterns, trends, and potential issues that could affect the business’s financial health. This ability helps them to spot inconsistencies or irregularities in records, providing critical insights that can inform strategic decisions. Strong analytical skills empower bookkeepers to proactively advise on cost-saving opportunities and financial risks.
Technological Proficiency
Technological proficiency is increasingly essential for bookkeepers in today’s digital age. With numerous software solutions available for financial management, bookkeepers must be adept at using tools like QuickBooks, Xero, or Sage. These platforms automate many bookkeeping tasks, enhancing efficiency and accuracy. A comprehensive understanding of these technologies ensures seamless data entry, report generation, and financial monitoring. Furthermore, the use of email communication allows bookkeepers to quickly resolve queries and verify that all financial entries align correctly. Access to online translation tools can facilitate the management of multilingual financial documents, broadening the reach of services on a global scale. This proficiency also allows bookkeepers to stay current with industry trends, leverage technological advancements for enhanced productivity, and employ templates for streamlining financial report creation. By incorporating data from translation corpora, bookkeepers can ensure all documentation maintains consistency and accuracy across different languages. Supplementary skills in spreadsheet management also support effective financial wrangling, reducing the time spent on manual data handling.
Communication Abilities
Effective communication abilities are crucial for bookkeepers, as they frequently interact with business owners, accountants, and other stakeholders. This involves more than just speaking clearly; it includes obtaining consent to discuss financial standings and regularly seeking feedback to ensure all parties are on the same page. A bookkeeper must convey complex financial information in a clear and accessible manner, ensuring that everyone involved understands the business’s financial status. Good communication also involves listening carefully to others’ needs and concerns, enabling them to address issues and provide tailored financial advice. This skill fosters collaboration and transparency, essential components for maintaining a healthy financial environment.
The Difference Between Bookkeepers and Accountants
Distinct Roles and Responsibilities
While bookkeepers and accountants both play vital roles in financial management, their responsibilities differ significantly. Bookkeepers focus on recording day-to-day transactions, ensuring detailed and accurate financial records. Their duties include managing accounts payable and receivable, processing payroll, and reconciling bank statements.
In contrast, accountants take a broader view of financial management. They analyze the records maintained by bookkeepers to prepare financial statements, develop budgets, and provide strategic financial advice. Accountants often handle tax preparation and ensure regulatory compliance, offering insights that guide long-term business decisions.
Educational Pathways
Bookkeepers and accountants have different educational pathways, tailored to their distinct roles. Bookkeepers—defined as a noun referring to professionals responsible for maintaining financial records—typically require a high school diploma and may benefit from postsecondary coursework in accounting or finance. Enrolling in a prep course can also help aspiring bookkeepers enhance their understanding of financial systems. Many pursue certification programs, such as Certified Bookkeeper (CB) from the American Institute of Professional Bookkeepers, to enhance their credibility and skills. Accountants, however, usually need a bachelor’s degree in accounting or a related field. Advanced roles may require a Certified Public Accountant (CPA) license, which involves passing a rigorous exam and meeting specific education and experience prerequisites. This licensing sets accountants apart, equipping them with the expertise to handle complex financial analysis and strategic advisory roles.
Becoming a Bookkeeper: Steps to Enter the Field
Educational Requirements
To embark on a career as a bookkeeper, a high school diploma is typically the minimum requirement. However, completing coursework in accounting, finance, or a related field can significantly boost your prospects. Many aspiring bookkeepers opt for associate degrees in accounting to gain foundational knowledge and enhance their employability. Vocational training programs and workshops also provide practical skills and understanding of bookkeeping fundamentals.
Certification Options
Certification can elevate a bookkeeper’s credentials and demonstrate their expertise. The Certified Bookkeeper (CB) designation from the American Institute of Professional Bookkeepers is one of the most recognized certifications. This requires passing an exam and having at least two years of bookkeeping experience. Another option is the QuickBooks Certified User, ideal for those specializing in accounting software.
These certifications not only enhance job prospects but also instill confidence in employers about a bookkeeper’s competence and professionalism. They reflect a commitment to quality and accuracy in financial record-keeping.
Gaining Practical Experience
Practical experience is crucial for honing bookkeeping skills and transitioning from theoretical knowledge to real-world application. Many aspiring bookkeepers start with internships or entry-level positions where they assist experienced professionals. These roles provide exposure to real financial documents, accounting software, and daily transaction management. Networking and finding mentors in the field can also open doors to practical learning opportunities.
Participating in workshops, volunteering to manage accounts for small businesses or nonprofits, and seeking part-time bookkeeping assignments are excellent ways to build practical experience. The hands-on expertise gained through these avenues is invaluable for advancing in the bookkeeping profession.
Bookkeeping Systems and Tools
Single vs. Double Entry Systems
The single-entry and double-entry systems are foundational bookkeeping methods, each serving different financial tracking needs. The single-entry system is simpler, akin to a checkbook register, where each transaction is recorded once, typically for cash-based small businesses. This straightforward approach is easy to manage but offers limited insights into business finances.
In contrast, the double-entry system records each transaction twice, as a debit and a credit, ensuring that the accounting equation (Assets = Liabilities + Equity) stays balanced. This method provides a more comprehensive view of financial health, supporting accurate financial statements and complex financial analysis. While it requires more effort and understanding, the double-entry system is favored for businesses seeking thorough financial oversight.
Popular Software Solutions
In today’s tech-driven landscape, several popular software solutions simplify bookkeeping tasks, making them more efficient and less prone to error. QuickBooks, known for its user-friendly interface and versatility, is ideal for small to medium-sized businesses. It offers real-time financial reporting and integration capabilities with other applications.
Xero is another preferred option for its cloud-based access and robust reporting features, allowing collaboration from anywhere. FreshBooks is particularly suited for service-based industries, offering time-tracking tools alongside basic bookkeeping functions. Sage offers comprehensive features for larger businesses, providing advanced inventory management and budgeting tools.
These software solutions streamline operations, enhance accuracy, and save time, making them indispensable tools for modern bookkeepers.
Benefits of Hiring a Professional Bookkeeper
Enhancing Financial Accuracy
Hiring a professional bookkeeper dramatically enhances financial accuracy by ensuring all transactions are meticulously recorded and verified. Bookkeepers bring expertise in implementing error-prevention measures, reconciling accounts, and maintaining up-to-date ledgers. According to recent usage reports, businesses utilizing professional bookkeeping services have shown improvement in financial accuracy. These services ensure that their usage of financial records aligns with accepted grammar and standards, crucial for business analysis and decision-making. Accurate financial records reduce the likelihood of discrepancies during audits and tax filings, providing peace of mind and reliability in financial reporting. Furthermore, in smaller organizations, the absence of a controller often leads to a higher reliance on detailed bookkeeping to manage simpler transactions, reinforcing the importance of accurate records for tax preparedness and smart business decisions. Trusted resources like the dictionary offer definitions and insights that align with professional bookkeeping terminologies, contributing to standardized reporting.
Improving Business Efficiency
A professional bookkeeper significantly boosts business efficiency by managing financial tasks with expertise and precision. This allows business owners to focus on their core operations without getting bogged down by complex accounting chores. Bookkeepers implement streamlined processes for invoicing, payments, and financial reporting, reducing processing time and minimizing human error. Their ability to maintain organized records aids in quick financial analysis and decision-making, ultimately leading to improved operational efficiency and strategic planning. Furthermore, having an updated website that highlights these efficient processes can attract potential clients and partners who value transparency and organization.
FAQs
What is book keeper?
A bookkeeper is a professional responsible for recording and maintaining a business’s financial transactions, such as sales, purchases, income, and payments. These professionals act like the financial noun of a business, ensuring accuracy in records and enabling informed financial decisions. They also employ tools like a thesaurus of financial terms to enhance clarity and consistency in documentation. Bookkeepers play a crucial role in managing finances efficiently and enable informed business decisions by utilizing synonyms to make complex financial terms accessible.
How does bookkeeping differ from accounting?
Bookkeeping involves recording daily financial transactions and maintaining accurate financial records. Accounting, on the other hand, encompasses a broader analysis of those records to prepare financial statements, provide financial insights, and guide strategic business decisions. While bookkeeping focuses on transaction management, accounting interprets and reports on the financial health of a business.
Can technology replace traditional bookkeeping?
Technology enhances bookkeeping efficiency by automating tasks and reducing errors, but it cannot replace the strategic insight and nuanced judgment that human bookkeepers provide. While software manages entries and reporting, professional bookkeepers interpret data, ensure compliance, and offer personalized financial advice tailored to business needs.
What are common mistakes made by bookkeepers?
Common mistakes by bookkeepers include data entry errors, neglecting to reconcile accounts regularly, and miscategorizing transactions. Inaccurate or delayed reports can lead to poor financial decisions. Being meticulous, maintaining organized records, and using reliable bookkeeping software can help avoid these pitfalls.
What is a bookkeeper job description?
A bookkeeper’s job description includes recording financial transactions, reconciling bank statements, and maintaining accurate ledgers. They manage accounts payable and receivable, prepare financial reports, and support audits. Bookkeepers ensure compliance with financial regulations and provide foundational data for strategic financial planning.
What are the main bookkeeper duties and responsibilities?
Main duties and responsibilities of a bookkeeper include recording daily financial transactions, processing invoices, and managing accounts payable and receivable. They reconcile bank statements, maintain organized financial records, and prepare monthly and annual financial reports. Additionally, bookkeepers assist in budgeting processes and ensure compliance with financial regulations.